Đừng than khóc khi sự việc kết thúc, hãy mỉm cười vì sự việc đã xảy ra. (Don’t cry because it’s over, smile because it happened. )Dr. Seuss
Người có trí luôn thận trọng trong cả ý nghĩ, lời nói cũng như việc làm. Kinh Pháp cú
Chúng ta không thể giải quyết các vấn đề bất ổn của mình với cùng những suy nghĩ giống như khi ta đã tạo ra chúng. (We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them.)Albert Einstein
Cỏ làm hại ruộng vườn, tham làm hại người đời. Bố thí người ly tham, do vậy được quả lớn.Kinh Pháp Cú (Kệ số 356)
Nếu muốn đi nhanh, hãy đi một mình. Nếu muốn đi xa, hãy đi cùng người khác. (If you want to go fast, go alone. If you want to go far, go together.)Ngạn ngữ Châu Phi
Đôi khi ta e ngại về cái giá phải trả để hoàn thiện bản thân, nhưng không biết rằng cái giá của sự không hoàn thiện lại còn đắt hơn!Sưu tầm
Như bông hoa tươi đẹp, có sắc nhưng không hương. Cũng vậy, lời khéo nói, không làm, không kết quả.Kinh Pháp cú (Kệ số 51)
Càng giúp người khác thì mình càng có nhiều hơn; càng cho người khác thì mình càng được nhiều hơn.Lão tử (Đạo đức kinh)
Bạn có thể trì hoãn, nhưng thời gian thì không. (You may delay, but time will not.)Benjamin Franklin
Nay vui, đời sau vui, làm phước, hai đời vui.Kinh Pháp Cú (Kệ số 16)
Lửa nào bằng lửa tham! Chấp nào bằng sân hận! Lưới nào bằng lưới si! Sông nào bằng sông ái!Kinh Pháp cú (Kệ số 251)
Trang chủ »» Danh mục »» »» English version »» Six Ways to Boost Blood Flow »»
English version
»» Six Ways to Boost Blood Flow
 Xem Mục lục
Xem Mục lục  Vietnamese || Đối chiếu song ngữ
Vietnamese || Đối chiếu song ngữ
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Path of Peace: A Journey of Healing Across America
- none
- none
- none
- none
- He Walks Like Christ, He Walks with the Buddha
- none
- The Rules Don't Shiver
- Will you be my dad until I die?
- none
- none
- The Old Man at the Thrift Store
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- More Than Half a Century of the World Buddhist Sangha Council
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Equity in Existence and Mortality (Life and Death)
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Buddhist Just Society
- The Buddhist Just Society
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Broken Gong
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- How to Do Metta
- none
- none
- none
- »» Six Ways to Boost Blood Flow
- none
- none
- none
- Thich Nhat Hanh’s Love Letter to the Earth
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Introduction: The Central Place of the Ideas of Karma and Rebirth in Buddhist Thought
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Chapter 25: Human Rights
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Dear beloved Thay
- Dear beloved Thay
- none
- Bāhiya's Teaching: In the Seen is just the Seen
- Bāhiya's Teaching: In the Seen is just the Seen
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Buddha on Politics, Economics, and Statecraft
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Tonglen on the Spot
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- War, Violence, Hatred, Non-violence, and Compassion.
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Vasubandhu
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Volodymyr Zelensky’s inaugural address
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Cat Who Went To Heaven
- none
- none
- none
- Speech by Dr. Carola Roloff
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Practical Vipassana Meditation Excercises by Mahasi Sayadaw
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Art of Living
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- BIOGRAPHY OF THE MOST VENERABLE BHIKSUNI THÍCH NỮ DIỆU TÂM
- none
- PIANO SONATA 14
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Hermit Who Owned His Mountain
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- A story about Nagarjuna
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Dhamma Talk of Master Thich Nhu Dien
- none
- none
- Magical Emanations: The Unexpected Lives of Western Tulkus
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Introduction to the selections from Vajrayāna Buddhism
- Introduction to the selections from Mahāyāna Buddhism
- Introduction to the selections from Theravāda Buddhism
- Introduction to the Sangha, or community of disciples
- Introduction on the life of the historical Buddha
- INTRODUCTION
- none
- none
- Dharma Talk at Beel Low See Temple, Singapore
- none
- none
- Buddhist Perspectives on Contemporary Issues
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- How Lankan Buddhists won the battle against proselytization
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Managing Emotions Effectively in Uncertain Times
- What Happens After Coronavirus?
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Thirty-Seven Practices of All the Bodhisattvas
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Invitation to Presencing for Each Other 6
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Desert Willow
- none
- Antonio and His Treasure
- none
- Tim and Grandpa Joe
- none
- none
- none
- Amrita and the Elephants
- Egbert and the Fisherman
- The Spirit of the Tree
- Danan and the Serpent
- none
- none
- The Beautiful White Horse
- none
- none
- none
- The Monkey Thieves
- Angelica and King Frederick
- Aloka and the Band of Robbers
- none
- The Shiny Red Train
- The Sheep Stealers
- none
- Ester and Lucky
- The new girl
- none
- The Enlightenment of Chiyono
- The Magic Moonlight Tree
- none
- none
- none
- Bella and the Magic Soup
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Man-made Obstacle Distinguishing between problems of human birth and problems of human making
- none
- none
- How to Practice Chanting
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Marx and Walking Zen
- none
- none
- The Math Koan
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Phổ Môn Kệ Tụng
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- How Buddhists Can Benefit from Western Philosophy
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Birth of an American Form of Buddhism: The Japanese-American Buddhist Experience in World War II
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Flood of Tears
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Can our brains see the fourth dimension?
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Our dedication
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Peace in each breath is peace in life Practice breathing for good sleep and peace in life.
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Price of a Miracle
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Reminiscing Elder Brother Cao Chanh Huu
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Everything is Changeable
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- 太上感應篇(第一集)新加坡淨宗學會
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- A Devoted Son
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Art of Living: Vipassana Meditation
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- “Returning Home” a Dharma retreat for the Youth in America
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- TET, a Vietnamese Tradition
- Wake Up - The Awakening from Within
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- How a Hollywood Mogul Found True Happiness
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Lonely Journey of Thousand Miles
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Discourse on Loving Kindness (Metta Sutra)
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Ambrosia Rain – The Merit of Life-Release
- Place Holder of Thousands of Stars
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Your Light May Go Out
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- The Ultimate Happiness
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Dalai Lama: 5 things to keep in mind for the next four years
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- Buddhism scripture teachers struggling to keep up with demand from state schools
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- LETTER TO THỪA THIÊN - HUẾ'S BUDDHIST STUDENTS
- Why Larung Gar, the Buddhist institute in eastern Tibet, is important
- none
- none
- Buddhism and the Youth
- Five Precepts
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
- none
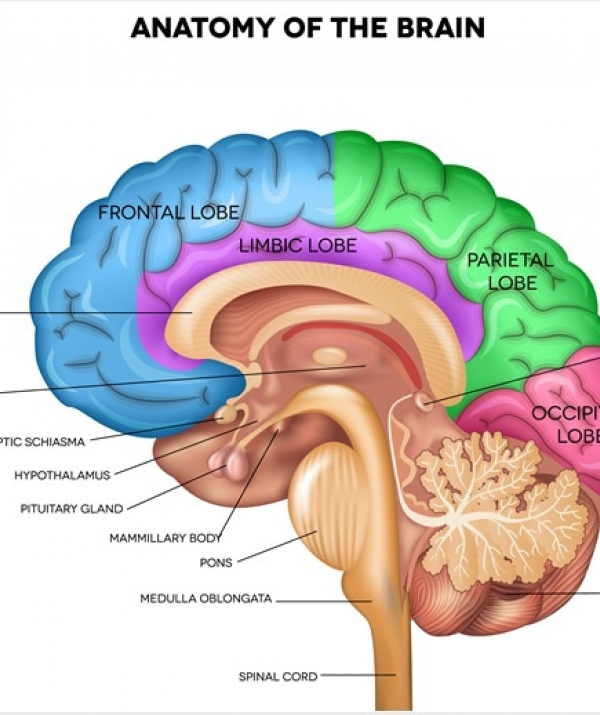
Our brain has many well-known structures like the amygdala that detects danger and the prefrontal cortex that enables planning, but we often take for granted the 400 miles of blood vessels that push through a liter of blood per minute, carrying in oxygen and nutrients, and porting out wastes. “Our brains are highly metabolic organs, so they require lots of nutrients and oxygen to function properly, and those can only get to our brain when we have good blood flow,” says naturopathic physician Emilie Wilson, of the Synergy Wellness Center, in Prescott, Arizona.
When that blood flow is optimal, we feel energized and clear-headed; when it’s low, we feel foggy and listless. Low levels of cranial blood flow have been linked in brain imaging studies to strokes and dementia, as well as bipolar disorder, depression and suicidal tendencies. The first imperative for healthy cranial blood flow is to make sure our blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol numbers are in a healthy range. Health practitioners can help us address that, as well as the conditions linked to reduced blood flow—heart disease, hypothyroidism, diabetes, anemia, depression and smoking. To boost brain blood flow, specific lifestyle strategies have proven to be highly effective:
1. Eat strategically, especially beets and chocolate.
Nitric oxide (NO) is made in the endothelium, the thin layer of cells that line blood vessels; it relaxes the inner muscles of those vessels, maximizing blood flow. “The continuous formation of NO in the brain is essential to life,” says prominent pharmacologist Louis Ignarro, Ph.D., who received the Nobel Prize in Science in 1998 for discovering that humans produce NO and that it lowers blood pressure and improves blood flow. He advocates passing up meat for soy and fish protein, eating antioxidant-rich produce such as pomegranate, blueberries, spinach and kale, and consuming lots of nitrate-rich food like celery and leafy greens which are converted to NO in the body. He especially recommends beets—one study reported that in juice form, it increases nitric oxide levels by 21 percent in 45 minutes—as well as dark chocolate. In a Harvard study, older people that drank two cups of hot chocolate a day for 30 days had improved blood flow to the brain and better memory.
2. Take amino acid supplements.
“Consuming supplements containing both L-arginine and L-citrulline are welldocumented to boost the production of endothelium-derived NO,” says Ignarro. “Adding antioxidants to the amino acid mix provides added benefit by increasing NO levels.” He recommends pomegranate extract, cocoa flavonols and omega-3 supplements.
3. Move the body.
Fast walking, running, cycling, swimming, ball playing, weight lifting and yoga all help improve cranial blood flow, says Ignarro: “Physical activity stimulates the production of NO in all arteries, including those in the brain.” In one study, women over 60 that walked for 30 to 50 minutes three or four times a week increased ongoing cranial blood flow up to 15 percent. Yoga exercises like downward dog and shoulder stands also raise blood flow in the head.
4. Play music.
Research using functional magnetic resonance imaging published in Scientific Reports found that blood flow in the brain increases when people listen to music they love, whether it’s Mozart or Eminem. In a recent study, Weightless, a song written by the British group Macaroni Union along with sound therapists, reduced participants’ anxiety levels by 65 percent and physiological resting rates by 35 percent.
5. Do a chanting meditation.
Kirtan Kriya, a 12-minute daily meditation that includes chanting, finger movements and visualization, “has been researched for over 18 years and has documented benefits in increasing blood flow to the brain,” says Krystal Culler, senior Atlantic fellow with the Global Brain Health Institute, in San Francisco and Ireland. YouTube offers several versions, as does the Alzheimer’s Research and Prevention Foundation (Tinyurl.com/12MinuteYogaMeditation).
6. Consider acupuncture and craniosacral therapy.
“Acupuncture has been used for thousands of years to boost blood flow, and it can also relax tense muscles in the neck and head, which can impair blood flow more than we realize,” says Wilson. She also recommends the gentle, hands-on-head approach of craniosacral therapy: “It can directly improve blood flow by removing restrictions, and it can also re-balance sympathetic and parasympathetic functions, which has beneficial effects on our nervous system and on blood flow.”
MUA THỈNH KINH SÁCH PHẬT HỌC
DO NXB LIÊN PHẬT HỘI PHÁT HÀNH
Mua sách qua Amazon sẽ được gửi đến tận nhà - trên toàn nước Mỹ, Canada, Âu châu và Úc châu.
Quý vị đang truy cập từ IP 216.73.216.143, 69.15.33.12 và chưa ghi danh hoặc đăng nhập trên máy tính này. Nếu là thành viên, quý vị chỉ cần đăng nhập một lần duy nhất trên thiết bị truy cập, bằng email và mật khẩu đã chọn.
Chúng tôi khuyến khích việc ghi danh thành viên ,để thuận tiện trong việc chia sẻ thông tin, chia sẻ kinh nghiệm sống giữa các thành viên, đồng thời quý vị cũng sẽ nhận được sự hỗ trợ kỹ thuật từ Ban Quản Trị trong quá trình sử dụng website này.
Việc ghi danh là hoàn toàn miễn phí và tự nguyện.
Ghi danh hoặc đăng nhập
... ...


 Trang chủ
Trang chủ






